In the first part we discussed pods communication through Kubernetes services, all of this internally in the cluster, but what if we need to expose the service to the internet?
Exposing services to the internet Link to heading
Node Port
The service type NodePort creates a unique port in every node of the cluster and forwards the requests to the pods that are part of that service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: example-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort ❶
ports:
- port: 80 ❷
targetPort: 80 ❸
nodePort: 30021 ❹
selector:
app: example
❶ Set the service type to NodePort.
❷ Port of the service’s internal cluster IP.
❸ Target port of the backing pods.
❹ The service will be accessible through port 30021 of each of your cluster node (no requiered, if missing Kubernetes will choose a random port)
$ kubectl get service example-nodeport
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
example-nodeport 10.110.254.212 <nodes> 80:30021/TCP 14m
Now you can access the service via the Node public IP address.
Let’s assume that the public IP address of one of our nodes is 35.203.63.213
curl http://35.203.63.213:30021
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
</head>
...
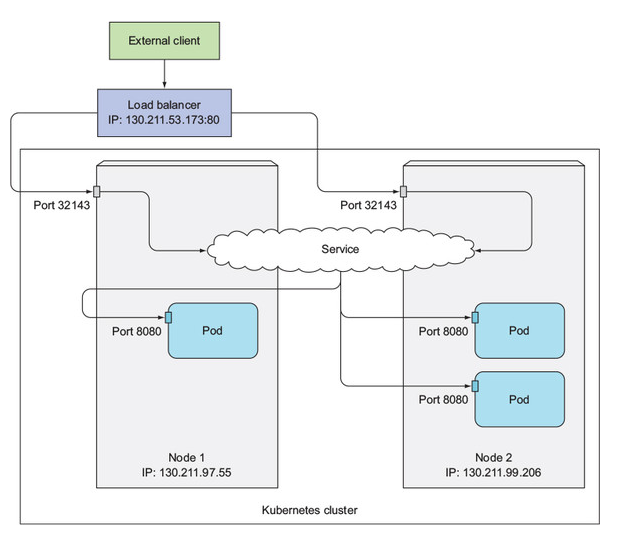
LoadBalancer
The LoadBalancer service type is an extension of the NodePort type service. Is only supported in Kubernetes clusters running in Cloud Service providers like AWS and GCP.
If the Kubernetes cluster does not support the LoadBalancer service type then a NodePort service will be created instead.
Ingress Resource
The Ingress resource is a controller that runs in the cluster.
It operates at the layer 7 (application) level offering different options to route traffic to one or more services using a single endpoint.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example
spec:
rules:
- host: service.libert.xyz
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: example-nodeport
servicePort: 80
Now you can access the ingress using the hostname.
$ curl http://service.libert.xyz
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
</head>
...
The workflow starts with a DNS lookup of service.libert.xyz to getthe IP of the Ingress controller.
The client then sent an HTTP request to the Ingress controller and specified service.libert.xyz in the Host header.
From that header, the Ingress controller determines which service the client is trying to access, looked up the pod IPs through the Endpoints object associated with the service, and forwards the client’s request to one of the pods.
In the following example, we can see how we can route the traffic to different services using a single endpoint.
...
- host: service.libert.xyz
http:
paths:
- path: /health ❶
backend: ❶
serviceName: foo ❶
servicePort: 80 ❶
- path: /bar ❷
backend: ❷
serviceName: bar ❷
servicePort: 80 ❷
*** References - Kubernetes in Action